Castoreum in perfumery

In This Article
Understanding Castoreum
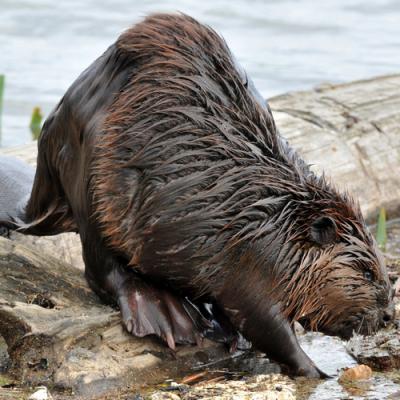
Castoreum is an oily and fragrant secretion produced by the castor sacs found in two species of beavers: the Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) and the North American beaver (Castor canadensis). These sacs are located near the animals' genital tracts and serve essential biological functions. They help beavers identify one another, mark their territories, regulate their population, and facilitate reproduction through pheromonal activity.
Besides these functions, castoreum also waterproofs the beavers' fur. It has been utilized for various purposes since ancient times, with mentions in Byzantine-era medical texts. Castoreum has been used in perfumes since that period, and beavers were also hunted for their fur and meat. Trappers once utilized castoreum to lure carnivorous animals to their traps. Historically, it was believed to treat uterine diseases, fevers, headaches, epilepsy, and surgical wounds. However, castoreum is no longer considered a therapeutic agent and is primarily used in the perfume industry.
The Sensual Scent of Castoreum
Due to its high cost, castoreum is typically found in prestigious perfumes, such as Antaeus by Chanel, Bel Ami by Hermès, or Dolce Vita by Dior.
Fun Facts About Castoreum
- Castoreum's name is derived from the Latin word "castor," which means beaver.
- In the past, castoreum was believed to have medicinal properties and was used in various treatments, although it is no longer used for therapeutic purposes today.
- Food manufacturers sometimes use castoreum as a flavoring agent in certain foods, particularly as a substitute for vanilla.
- The FDA classifies castoreum as a "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) substance for use in food and beverages.